I have found a new method of transferring drawings to canvas besides the oil transfer. Jeremy Deck showed me how to do a wintergreen oil transfer. Footnotes are included in this post to indicate which sentences in this post are summarizations of ideas that Jeremy Deck explained to me.
A wintergreen oil transfer begins by photocopying the drawing in reverse. Then one applies two sheets of foam core up and inside of the stretcher bars to brace the canvas when it will be pressed on during the transfer.¹ The canvas must be places above the ground and should be supported by something in the center.¹ The photocopy is then placed face down on the canvas with a bit of a border and the edges of the photocopy are taped down so it will not move.¹ Then wintergreen oil is quickly applied with a bristle brush.¹ Since too much wintergreen oil results in the transfer to become smeared and too little results in a weak transfer the idea is to scrub the wintergreen oil onto the photocopy so it is not too much.¹ Then paper towels are applied to the back of the photocopy for about 30-50 seconds to absorb excess oil.¹ Then the copy is scraped from the top to the bottom with the edge of a spoon.¹ Pressure is to be applied to areas of the photocopy in multiple passes and one is to do the same from the opposite side as well.¹ The photocopy can be removed and the transfer is permanently fixed to the canvas and turpentine has no effect on it.¹ This is very useful if one does not want to lose all of the subtle tilts found during the final pass of a block-in.¹
Footnotes
¹ Jeremy Deck, personal communication, 2012.
Wednesday, February 6, 2013
Composition studies
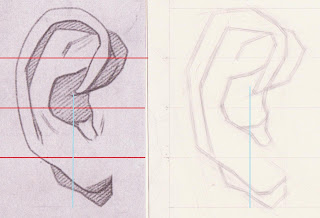
Ear Cast Drawing Process, Part 1
This post is a summary of the process of modelling form in graphite that I have learned at The Cambridge St. Studios. Footnotes are included in this post to indicate which sentences in this post are summarizations of ideas that the instructors at The Cambridge Street Studios have explained to me.
Modeling form is based upon an understanding of an object's relationship to a light source. Every form is spherical and has a specific relationship to a light source(s).
The majority of forms that one sees exhibit diffuse
reflection. Diffuse reflection occurs when light rays projected from a
light source reflect at various angles from its meeting with the
surface of form due to irregularities in the microscopic surface of a form.
The example above show only a fraction of the portion of light rays emitted from a light source. In diffuse reflection, millions of light rays, composed of photons, are projected from the light source to meet the surface of a form and then reflect at various angles.
More Information About Light On Form
The terminator exists at the apex of where light rays from the light source do not reach. Therefore the terminator defines the area of object that is in shadow.

On the sphere the eye does not perceive the halftone to exist in the middle of a gradation as it often is drawn in most how to draw books. In fact under a spot light scenario the eye perceives halftone to start very close to the terminator. Usually under a spot light scenario the halftone begins at 18 degrees away from the terminator, but situations can vary so much that one would have to determine how close the halftone is to the terminator just by observing it. To my knowledge, the half tone in a spot light scenario actually occurs at 30 degrees from the terminator but I am not sure why it is usually perceived at 18 degrees before the terminator. Nevertheless, this knowledge that the eye perceives halftone to exist very close to the terminator allows for a more accurate representation of the forms one is modelling.
With an understanding of diffuse reflection, the fact that half tone exists very close to the terminator and an acuteness to each forms relationship to the light source one can begin to model form.
But before the actual modelling of form begins upon a block-in, I made a poster study of the values to be used while modelling. To explain the modelling process I will use the cast drawing that I am currently working on as an example.
Above is the poster study that my instructor Jeremy Deck made as an example of a poster study. The infinite value range seen in life is due to the fact that forms are not vertical. They can get lighter by facing more towards the light or turning more away from the light. Because there is a limit to the value range that can exist on the vertical surface of a piece of paper one must approach modelling with the understanding that the value range in their drawing will be compressed as well. To this end, one can make the value range darker or lighter but it will remain compressed because the paper that one draws on is vertical. So the poster study is made to represent five key values. The first value that is determined the cast shadow value on a black surface so that one can know the etxtremities of how dark one's value range could possibly go.¹ An HB pencil was used to make this value and this value set the standard of the value range to be used in the drawing. The next values that were decided upon were the darkest value of the wall shadow, the average value of the cast shadow on the cast, the value of the highest form light and the value of the highlight(which is the white of the paper).¹ The values after the value of the shadow of a black object were decided upon by their relationship to one another (not by copying perceived values on the cast).¹ A line was erased from the value of the highest form light to decide if the value was dark enough for the erased line to read as a highlight.¹
One should know that due to the fact that the highlight has a major difference in tone in relation to the highest form light, choosing to make the highlight as evident as it appears in life causes the value of the highest form light to be quite dark and therefore causes the entire drawing to darken in compression.¹ This produces a darker drawing that will accurately show the distinction between the highlight and the form light but since the drawing as a whole will be darker the drawing will not appear to represent a white object under a spotlight. This darkening can be avoided by setting the value of the highest form light to the white of the paper and sacrificing the clarity of the highlight next to the highest form light.¹ I chose to preserve the distinction of the highlight next to the highest form light in this drawing.
One may wonder why an HB pencil would be the softest pencil to be used in a drawing of a white cast that does not encompass the entire value range. The reason is because cast drawing is also practice for painting. And with paint, one's value range is still limited because of working on a vertical plane and if one wanted to paint a subject that had more than one local color they would need skill at modelling form within a limited value range in order to not exhaust one's entire value range on an object of one local color and thus not leaving enough of the range left for objects of darker or lighter local colors.¹
Using the poster study as a guide for the value of the average cast shadow I began to fill in the shadow areas of the drawing with that value. It is necessary to flatten the entire shadow area with this value because when one is modelling form it is helpful to have a common value that one is modelling all of the forms out of. If I was to draw all of the difference in the shadow at first I would have a more difficult time understanding what the value of the darkest form light is supposed to be. Not to mention the fact that if I finished the shadow first without referring to the values that are in the light part of the form I would more than likely exaggerate the value of the reflected light.
Flattening proceeds by filling in small squares (about 1/8th of an inch wide) first with a slightly dulled pencil.¹ One is to initially fill in squares from one side to the other to the value desired.¹ This is not a type of drawing that is to be worked up in veils and is to be very direct even when modelling areas of a form that are not in shadow.¹ The evenness of this first application is a result of the right amount of pressure combined with the right amount of speed up and down while moving to the other side.¹ After the initial application there usually are many tiny dots that need to be filled in if the square is to read as completely flat. To fill it in one is to use a slightly sharper pencil and to pull out darker dots one is to use a blunted dirty kneaded eraser so as not to remove too much graphite that would create more dots to fill in.¹ The slightly sharper pencil is not to poke into the lighter dots as it is to do more the job of gently pushing the graphite from the tip of the pencil into the lighter dots to fill them in.¹ It is useful to view these squares at an angle to notice obvious dots.¹ It is also useful to throw one's eyes out of focus to notice obvious dots.¹ The squares of value are placed next to each other to stay connected.¹ Practice and experimentation with different hardness of lead and different speeds of application is the only way to improve at this. For this, I used an H pencil.
The pencil is to be sharpened then slightly dulled by rubbing it on the paper as seen in the image above because one does not want to damage the paper.¹ I am working on Artistico Fabriano Extra White, 140 lb. Hot Press paper and too much pressure can really damage this paper. This was something that I had to be very careful of while making the block-in for this drawing. It is very useful to have a really sharp pencil before dulling it down a bit. I use an Eagle 17 lead pointer to sharpen my pencil and it creates a very sharp point. Eagle 17 lead pointers can be purchased on ebay.
While flattening the shadows and even while modelling the lights the pencil is to be held at about a 45 degree angle from the paper as seen in the image above.¹ A visual example of this application of graphite can be seen in this video of students working at GCA here.
One can go right over any lines that define important information in the shadows without any fear of losing the block-in because the lines show though. Below is my flattened drawing near the before modelling form.I really only had to flatten around the area that I would be modelling first so I didn't flatten all of the shadows. After this stage I lightened the outlines from the block-in that were around the area that I was going to model so I get a better idea of what the form actually looks like.¹
Now I should explain the three step modelling process that I am practicing on this cast drawing.
Step 1 is Gradation. This is just rolling from the darkest form light to the form light most facing the light source with an understanding that the darkest form light exists just outside of the average shadow value and therefore must be just barely lighter than the average shadow value.¹ Gradations in this method are not decided upon by questioning if something is lighter or darker but questioning whether forms are faced more or less towards the light. And if a form needs to turn away that means it needs to get darker, if a form needs to turn more towards the light that means it needs to get lighter. The mindset for this drawing method is just as if one is sculpting the form on their drawing to accurately mimic the sculptural form(s) on a cast. Please note that all the modelling is to be done in small strips that describe the cross contour of a form.¹ In the gradation stage the strip is to laid in with strokes that run at a perpendicular angle to the direction of the largest amount of change in light on a form.¹ For example, in my diagram the sphere is lit from above, so the greatest amount of change in light on form is from top to bottom. Therefore, I laid strip number 1 with strokes that ran from left to right. It is much easier to address the holes that occur in the gradation stage when one will be marbling through them instead of against them.¹
Step 2 is Planarization or the grouping of planes. In this step one is to break the gradation into three to four distinct planes.¹ I now must say that in this drawing method each dot of graphite is not to be referred to as a value alone. Instead, in this drawing method each dot of graphite represents a micro-plane that has a specific relationship to the light. So when one is planarizing the goal of cleaning up the planes is to group each micro-plane into its respective larger plane instead of thinking of filling in or taking out dark or light spots in a value. At the completion of this stage the strip is to look like a planar version of the form. In my diagram I did not include the terminator value and reflected light in this step but usually those are added during this step.
The terminator value is found by referring back to the poster study and determining the value relationship between the darkest part of the wall shadow and the darkest terminator value.¹
Step 3 is Marbling. The transition from the planarization stage to the marble stage is focused on softening the harsh planar breaks, only as needed, in order to more specifically address the subtle changes in the form that one sees.¹ In this step one gains a tactile sense of the form by imagining the point of their pencil on a specific place of their drawing, looking to the same specific place on the cast and running one's eye(that is on the cast) at the same pace and direction that the pencil is moving on the drawing across a form(s) while one shifts their gaze from the cast to the drawing in order to determine whether some of the micro-planes in one's drawing need to turn more or less away from the light.¹ It is usually best to start at a definite point such as the terminator or the high form light because the only variable is for form to turn towards or away from the light from those definite points.
If this practice is specifically adhered to then one can gain the sensation of being on the form while they are marbling. The more that one marbles the more polished the form becomes. Or rather, the more specific the micro-planes adhere to their relationship to the light source. One is to begin marbling a strip by marbling along a path that describes the gradation of form with the most change. Once the major change of a strip has been accurately addressed one can marble the strip in every direction in order to address each micro-plane.¹ After this, one is to address each and every micro-planes relationship to the light source within that strip.¹ Once the overall form of the strip is accurately represented, one can and should include all detail including all the bumps and dents seen on the cast.¹
After a strip has been completed a new strip is added next to it that goes through the three step modelling process and is restitched into the previous strip during the marbling stage.¹ Please note, that for all of the strips besides the first strip one should start by including the terminator value before running a gradation. One should continue to marble the combined strips of each form as the drawing progresses. While it is good to keep strips of form next to each other for each form, with every new form one should begin with a strip that describes the most amount of change in the light on that form in order to better perceive the value range for that form.¹ It is very useful to compare back to the planes from the first form while adding new forms, in order to develop an overall relationship hierarchy in one's drawing.
There is not a specific way of looking at one's drawing during this process. One should squint, throw their eyes out of focus, use a black mirror (a piece of mirror glass that is painted black on the back so as to darken the reflection that one sees. This is about the same as squinting but much clearer.) and use conceptual ideas about form in relation to light.¹ All of these ways of seeing are tools that one should use to check one's drawing. If any inconsistencies are found in your drawing while checking it with those tools then the drawing is not accurate. One should use these viewing tools with an understanding that the value range in the drawing will be much more compressed than what one sees in life so therefore any value observations are to be determined by relationship of one to another.¹ This is very important when drawing shadows because since they are so dark I usually resort more to my black mirror than marbling while drawing them. But one can think of the form in shadows related to a light source by determining the specific light source for reflected light. Using a black piece of tinfoil to block out that are to see when the reflected light vanishes is very helpful.¹
I started with these few strips because these strips describe an area of the cast that contains the majority of my value range and it is useful to base any strips added next to them on that value range. One is to start by taking only a few strips up to the marbling stage and then include the terminator value and reflected light.¹ Or one could flatten the shadow value in relation to the terminator value and put the reflected light in last if one is afraid of making the reflected light too light at first. Please note, that after the terminator value has been put in the strip has to be re marbled and the dark form light has to re turn into the terminator which makes it darker.¹ This is fine because the average shadow value is just general and it is fine if the darkest form light ends up being darker than the average shadow value.
The only other thing to consider is the difference in the quality of edges. This is done mainly by relating all of the edges to the hardest edge.
Below is my cast drawing in progress from last Friday. I was still marbling the lights and flattening the shadow. I have been using an H pencil for the gradation stage and a 3H to marble. So far the darkest pencil that I have used in the shadow has been an HB. The hardness of pencil to use is determined by deciding which lead will produce the values that I desire without the use of so much force that I would scratch the paper.¹
It is very useful to surround the area that one is modelling with a dark value in order to better see subtle gradations. This is because the eye splits up gradations into 1,000 sections based upon the range of values that it sees.¹ By compressing the range of values that the eye sees by surrounding a drawing with a dark border one can better see the subtle gradations in what they are drawing.¹ It is very useful to wear a hat with a brim while modelling to get rid of the reflected light that the planes facing the light on the texture of the paper are receiving so that one can better see the subtle gradations in what they are drawing.¹
Below are some tactile evaluation analogies that have been helpful to me while I was in the marble stage of this drawing.
Rain on Tiles- Imagining the rays of light as rain that is falling onto a form. When tiles on a roof are faced most towards the rain it makes a really loud noise and when the tiles are facing less parallel to the rain a gentler sound is heard.
The Ant- The ant is pretty much the same as the marble but by imagining the point of the pencil as an ant crawling on the form that is seen one can imagine how much energy the ant has to exert while crawling on a form. This helps to make subtle rolls easier to see.
The Skateboard- The skateboard analogy was conceived by Tony Ranalli. The skateboard is pretty much the same as the ant but is imagining skateboarding across a form while modelling instead of an ant crawling.²
Any analogies that one can relate to are helpful to refer to while modelling form. And another useful tactile evaluation tool is to touch the forms on the cast that one is modelling. Touching the cast can be of great use to more accurately interpret the gradations that one sees on the cast.
Footnotes
¹ Jeremy Deck, personal communication, 2012.
² Anthony Ranalli, personal communication, 2012.
Modeling form is based upon an understanding of an object's relationship to a light source. Every form is spherical and has a specific relationship to a light source(s).
The example above show only a fraction of the portion of light rays emitted from a light source. In diffuse reflection, millions of light rays, composed of photons, are projected from the light source to meet the surface of a form and then reflect at various angles.
Consequently, as the light rays from the light source have further to travel before meeting the surface of a form the less light is received by those areas on a form. This is due to the fact that light rays are composed of photons, which posses more light energy the closer they are to the light source. The areas on a form that are most facing the light source will reflect many light rays because many light rays can reach those areas that are facing the light source. As the parts of a form recede from the angle of the light source, they become darker in value due to the fact that they are receiving less light to reflect diffusely. It is this diffusely reflected light, created by the interaction of light on form, that enters the eye to make an image of the objects that one sees.
The illustration above shows in a constricted sense, if only 7 photons were projecting from the light source, more light rays would strike plane A than plane B, because plane A is more facing the angle of the light source. Since plane B is facing more away from the angle of the light source it receives less photons, and therefore less light, to reflect diffusely which causes plane B to appear darker in value.
More Information About Light On Form
The terminator exists at the apex of where light rays from the light source do not reach. Therefore the terminator defines the area of object that is in shadow.

On the sphere the eye does not perceive the halftone to exist in the middle of a gradation as it often is drawn in most how to draw books. In fact under a spot light scenario the eye perceives halftone to start very close to the terminator. Usually under a spot light scenario the halftone begins at 18 degrees away from the terminator, but situations can vary so much that one would have to determine how close the halftone is to the terminator just by observing it. To my knowledge, the half tone in a spot light scenario actually occurs at 30 degrees from the terminator but I am not sure why it is usually perceived at 18 degrees before the terminator. Nevertheless, this knowledge that the eye perceives halftone to exist very close to the terminator allows for a more accurate representation of the forms one is modelling.
With an understanding of diffuse reflection, the fact that half tone exists very close to the terminator and an acuteness to each forms relationship to the light source one can begin to model form.
But before the actual modelling of form begins upon a block-in, I made a poster study of the values to be used while modelling. To explain the modelling process I will use the cast drawing that I am currently working on as an example.
Above is the poster study that my instructor Jeremy Deck made as an example of a poster study. The infinite value range seen in life is due to the fact that forms are not vertical. They can get lighter by facing more towards the light or turning more away from the light. Because there is a limit to the value range that can exist on the vertical surface of a piece of paper one must approach modelling with the understanding that the value range in their drawing will be compressed as well. To this end, one can make the value range darker or lighter but it will remain compressed because the paper that one draws on is vertical. So the poster study is made to represent five key values. The first value that is determined the cast shadow value on a black surface so that one can know the etxtremities of how dark one's value range could possibly go.¹ An HB pencil was used to make this value and this value set the standard of the value range to be used in the drawing. The next values that were decided upon were the darkest value of the wall shadow, the average value of the cast shadow on the cast, the value of the highest form light and the value of the highlight(which is the white of the paper).¹ The values after the value of the shadow of a black object were decided upon by their relationship to one another (not by copying perceived values on the cast).¹ A line was erased from the value of the highest form light to decide if the value was dark enough for the erased line to read as a highlight.¹
One should know that due to the fact that the highlight has a major difference in tone in relation to the highest form light, choosing to make the highlight as evident as it appears in life causes the value of the highest form light to be quite dark and therefore causes the entire drawing to darken in compression.¹ This produces a darker drawing that will accurately show the distinction between the highlight and the form light but since the drawing as a whole will be darker the drawing will not appear to represent a white object under a spotlight. This darkening can be avoided by setting the value of the highest form light to the white of the paper and sacrificing the clarity of the highlight next to the highest form light.¹ I chose to preserve the distinction of the highlight next to the highest form light in this drawing.
One may wonder why an HB pencil would be the softest pencil to be used in a drawing of a white cast that does not encompass the entire value range. The reason is because cast drawing is also practice for painting. And with paint, one's value range is still limited because of working on a vertical plane and if one wanted to paint a subject that had more than one local color they would need skill at modelling form within a limited value range in order to not exhaust one's entire value range on an object of one local color and thus not leaving enough of the range left for objects of darker or lighter local colors.¹
Using the poster study as a guide for the value of the average cast shadow I began to fill in the shadow areas of the drawing with that value. It is necessary to flatten the entire shadow area with this value because when one is modelling form it is helpful to have a common value that one is modelling all of the forms out of. If I was to draw all of the difference in the shadow at first I would have a more difficult time understanding what the value of the darkest form light is supposed to be. Not to mention the fact that if I finished the shadow first without referring to the values that are in the light part of the form I would more than likely exaggerate the value of the reflected light.
Flattening proceeds by filling in small squares (about 1/8th of an inch wide) first with a slightly dulled pencil.¹ One is to initially fill in squares from one side to the other to the value desired.¹ This is not a type of drawing that is to be worked up in veils and is to be very direct even when modelling areas of a form that are not in shadow.¹ The evenness of this first application is a result of the right amount of pressure combined with the right amount of speed up and down while moving to the other side.¹ After the initial application there usually are many tiny dots that need to be filled in if the square is to read as completely flat. To fill it in one is to use a slightly sharper pencil and to pull out darker dots one is to use a blunted dirty kneaded eraser so as not to remove too much graphite that would create more dots to fill in.¹ The slightly sharper pencil is not to poke into the lighter dots as it is to do more the job of gently pushing the graphite from the tip of the pencil into the lighter dots to fill them in.¹ It is useful to view these squares at an angle to notice obvious dots.¹ It is also useful to throw one's eyes out of focus to notice obvious dots.¹ The squares of value are placed next to each other to stay connected.¹ Practice and experimentation with different hardness of lead and different speeds of application is the only way to improve at this. For this, I used an H pencil.
The pencil is to be sharpened then slightly dulled by rubbing it on the paper as seen in the image above because one does not want to damage the paper.¹ I am working on Artistico Fabriano Extra White, 140 lb. Hot Press paper and too much pressure can really damage this paper. This was something that I had to be very careful of while making the block-in for this drawing. It is very useful to have a really sharp pencil before dulling it down a bit. I use an Eagle 17 lead pointer to sharpen my pencil and it creates a very sharp point. Eagle 17 lead pointers can be purchased on ebay.
While flattening the shadows and even while modelling the lights the pencil is to be held at about a 45 degree angle from the paper as seen in the image above.¹ A visual example of this application of graphite can be seen in this video of students working at GCA here.
One can go right over any lines that define important information in the shadows without any fear of losing the block-in because the lines show though. Below is my flattened drawing near the before modelling form.I really only had to flatten around the area that I would be modelling first so I didn't flatten all of the shadows. After this stage I lightened the outlines from the block-in that were around the area that I was going to model so I get a better idea of what the form actually looks like.¹
Now I should explain the three step modelling process that I am practicing on this cast drawing.
Step 1 is Gradation. This is just rolling from the darkest form light to the form light most facing the light source with an understanding that the darkest form light exists just outside of the average shadow value and therefore must be just barely lighter than the average shadow value.¹ Gradations in this method are not decided upon by questioning if something is lighter or darker but questioning whether forms are faced more or less towards the light. And if a form needs to turn away that means it needs to get darker, if a form needs to turn more towards the light that means it needs to get lighter. The mindset for this drawing method is just as if one is sculpting the form on their drawing to accurately mimic the sculptural form(s) on a cast. Please note that all the modelling is to be done in small strips that describe the cross contour of a form.¹ In the gradation stage the strip is to laid in with strokes that run at a perpendicular angle to the direction of the largest amount of change in light on a form.¹ For example, in my diagram the sphere is lit from above, so the greatest amount of change in light on form is from top to bottom. Therefore, I laid strip number 1 with strokes that ran from left to right. It is much easier to address the holes that occur in the gradation stage when one will be marbling through them instead of against them.¹
Step 2 is Planarization or the grouping of planes. In this step one is to break the gradation into three to four distinct planes.¹ I now must say that in this drawing method each dot of graphite is not to be referred to as a value alone. Instead, in this drawing method each dot of graphite represents a micro-plane that has a specific relationship to the light. So when one is planarizing the goal of cleaning up the planes is to group each micro-plane into its respective larger plane instead of thinking of filling in or taking out dark or light spots in a value. At the completion of this stage the strip is to look like a planar version of the form. In my diagram I did not include the terminator value and reflected light in this step but usually those are added during this step.
The terminator value is found by referring back to the poster study and determining the value relationship between the darkest part of the wall shadow and the darkest terminator value.¹
Step 3 is Marbling. The transition from the planarization stage to the marble stage is focused on softening the harsh planar breaks, only as needed, in order to more specifically address the subtle changes in the form that one sees.¹ In this step one gains a tactile sense of the form by imagining the point of their pencil on a specific place of their drawing, looking to the same specific place on the cast and running one's eye(that is on the cast) at the same pace and direction that the pencil is moving on the drawing across a form(s) while one shifts their gaze from the cast to the drawing in order to determine whether some of the micro-planes in one's drawing need to turn more or less away from the light.¹ It is usually best to start at a definite point such as the terminator or the high form light because the only variable is for form to turn towards or away from the light from those definite points.
If this practice is specifically adhered to then one can gain the sensation of being on the form while they are marbling. The more that one marbles the more polished the form becomes. Or rather, the more specific the micro-planes adhere to their relationship to the light source. One is to begin marbling a strip by marbling along a path that describes the gradation of form with the most change. Once the major change of a strip has been accurately addressed one can marble the strip in every direction in order to address each micro-plane.¹ After this, one is to address each and every micro-planes relationship to the light source within that strip.¹ Once the overall form of the strip is accurately represented, one can and should include all detail including all the bumps and dents seen on the cast.¹
After a strip has been completed a new strip is added next to it that goes through the three step modelling process and is restitched into the previous strip during the marbling stage.¹ Please note, that for all of the strips besides the first strip one should start by including the terminator value before running a gradation. One should continue to marble the combined strips of each form as the drawing progresses. While it is good to keep strips of form next to each other for each form, with every new form one should begin with a strip that describes the most amount of change in the light on that form in order to better perceive the value range for that form.¹ It is very useful to compare back to the planes from the first form while adding new forms, in order to develop an overall relationship hierarchy in one's drawing.
There is not a specific way of looking at one's drawing during this process. One should squint, throw their eyes out of focus, use a black mirror (a piece of mirror glass that is painted black on the back so as to darken the reflection that one sees. This is about the same as squinting but much clearer.) and use conceptual ideas about form in relation to light.¹ All of these ways of seeing are tools that one should use to check one's drawing. If any inconsistencies are found in your drawing while checking it with those tools then the drawing is not accurate. One should use these viewing tools with an understanding that the value range in the drawing will be much more compressed than what one sees in life so therefore any value observations are to be determined by relationship of one to another.¹ This is very important when drawing shadows because since they are so dark I usually resort more to my black mirror than marbling while drawing them. But one can think of the form in shadows related to a light source by determining the specific light source for reflected light. Using a black piece of tinfoil to block out that are to see when the reflected light vanishes is very helpful.¹
I started with these few strips because these strips describe an area of the cast that contains the majority of my value range and it is useful to base any strips added next to them on that value range. One is to start by taking only a few strips up to the marbling stage and then include the terminator value and reflected light.¹ Or one could flatten the shadow value in relation to the terminator value and put the reflected light in last if one is afraid of making the reflected light too light at first. Please note, that after the terminator value has been put in the strip has to be re marbled and the dark form light has to re turn into the terminator which makes it darker.¹ This is fine because the average shadow value is just general and it is fine if the darkest form light ends up being darker than the average shadow value.
The only other thing to consider is the difference in the quality of edges. This is done mainly by relating all of the edges to the hardest edge.
Below is my cast drawing in progress from last Friday. I was still marbling the lights and flattening the shadow. I have been using an H pencil for the gradation stage and a 3H to marble. So far the darkest pencil that I have used in the shadow has been an HB. The hardness of pencil to use is determined by deciding which lead will produce the values that I desire without the use of so much force that I would scratch the paper.¹
It is very useful to surround the area that one is modelling with a dark value in order to better see subtle gradations. This is because the eye splits up gradations into 1,000 sections based upon the range of values that it sees.¹ By compressing the range of values that the eye sees by surrounding a drawing with a dark border one can better see the subtle gradations in what they are drawing.¹ It is very useful to wear a hat with a brim while modelling to get rid of the reflected light that the planes facing the light on the texture of the paper are receiving so that one can better see the subtle gradations in what they are drawing.¹
Below are some tactile evaluation analogies that have been helpful to me while I was in the marble stage of this drawing.
Rain on Tiles- Imagining the rays of light as rain that is falling onto a form. When tiles on a roof are faced most towards the rain it makes a really loud noise and when the tiles are facing less parallel to the rain a gentler sound is heard.
The Ant- The ant is pretty much the same as the marble but by imagining the point of the pencil as an ant crawling on the form that is seen one can imagine how much energy the ant has to exert while crawling on a form. This helps to make subtle rolls easier to see.
The Skateboard- The skateboard analogy was conceived by Tony Ranalli. The skateboard is pretty much the same as the ant but is imagining skateboarding across a form while modelling instead of an ant crawling.²
Any analogies that one can relate to are helpful to refer to while modelling form. And another useful tactile evaluation tool is to touch the forms on the cast that one is modelling. Touching the cast can be of great use to more accurately interpret the gradations that one sees on the cast.
Footnotes
¹ Jeremy Deck, personal communication, 2012.
² Anthony Ranalli, personal communication, 2012.
Drawing At The Picture Plane
This post is a summary of the comparative measurement
block-in process that I have learned from Jeremy Deck at The Cambridge St.
Studios. Footnotes are included in this post to indicate which sentences in this post are summarizations of ideas that the instructors at The Cambridge Street Studios have explained to me.
The Importance of Practicing Block-ins
The Block-in describes the outlines of an image that an artist
defines before modeling a subject. The
block-in is the foundation for modeling form.
One cannot achieve maximum accuracy of form without a completely
accurate block-in. The more accurate of
a map that one can layout to model on top of the more accurate the modeling can
be. If complete accuracy is not adhered
to in the block-in the planes that the shapes in the block-in describe will be
off and therefore the modeling on top of that block-in will not be accurate.
The practice of blocking in with an
emphasis on copying the shapes that one sees is very important. It is by copying the character of the shapes
that one sees that allows one to gain the highest accuracy in a block-in. It is no wonder that in the 19th
century, with the invention of photography that the accuracy in drawing
improved tremendously. ¹ It is not that artists were necessarily using
photography (although some artists did trace from photos) but the invention of
photography allowed for artists to see that specificity to the shapes that one sees allowed
for a higher level of accuracy.¹ It was
thought by artists prior to the 19th century that a profound
knowledge of anatomy would imbue their drawings with complete accuracy. But the copying of anatomy without building
the anatomy upon accurate representations of the shapes that one sees does not
result in accurate drawing. When only
the general idea of what accurate
anatomy looks like is applied to a block-in
the proportions that one is drawing become general as well and the practice of
blocking-in with that mindset will not result in the specific proportions of the
subject that one is copying. Take for
example this drawing by Michelangelo.
It
is completely accurate in the general idea of anatomy but no one looks like
that. If one was to follow Michelangelo’s
mode of thought one could perfectly draw the general anatomical idea of a bicep
and not draw a specific bicep seen in perspective on a specific
individual. Paying attention to the
visual shapes that anatomy conforms to on each individual seen in perspective helps to avoid this fault. Take these drawings by Bouguereau as an
example of the specific accuracy that focusing on the shapes that one is
copying allows for.
Notice how accurate
anatomy must conform to the shapes that one sees in order for a drawing to
represent a specific subject.
To ensure the most accuracy in
copying the shapes that one sees it is useful to use comparative measurement. The practice of comparative measurement
allows one to ensure that all of the shapes are accurate in relation to a
specific height to width measurement.¹ Without the use of comparative measurement and only the practice of
trying to copy the shapes that one sees through plumbing the height to width
relationship usually becomes in accurate.¹ To practice comparative measurement there are specific guidelines that
must be adhered to.
The Set- Up (please note that actual perspective was not
used in creating this diagram)
What one sees is limited to what is in one's cone of vision. A cone of vision describes the extremities of one's sight. The cone of vision spreads out equally in each direction the further it moves away from one's eye and is always parallel to one's gaze. In the diagram above the orange figure is drawing the box on the
wall and the yellow lines represent his cone of vision, the blue figure is
making a horizontal measurement of the box on the wall and the green lines
represent his cone of vision. The easel must be set-up at a perpendicular angle
to the subject so that the horizontal center of the subject is at the center of
one’s cone of vision.¹ This way one can
easily look from their drawing to the subject without having to arch their neck
or move their feet.¹ In this diagram the
drawing board is placed parallel to the orange figure’s cone of vision. If the center of one’s cone of vision is not
on the center of the drawing then the drawing could appear correct from the
angle that they are drawing at but when properly viewed by a viewer who is
parallel to the picture the proportions will look distorted.¹ This diagram also demonstrates that the angle
that measurements are made at must be parallel to the angle of one's cone of
vision. If the stick that the blue
figure in this diagram is holding was placed at a non-parallel angle to his
cone of vision, the accuracy of his measurement will be slighted by the
distortion of the angle that he is measuring on. Also note how close the orange figure is to
the subject that he is drawing. It is
advisable to get as close as possible, without distortion, when drawing because
the closer one is the crisper things look and it is easiest to draw something when one can see it as clearly as
possible.¹
Taping off the cast
This diagram illustrates what taping a vertical and
horizontal extremity that one sees of a cast does for the placement of the
cone of vision. By taping off the
horizontal and vertical extremities from the angle that one sees a cast the
cone of vision becomes cemented in a specific place.¹ In this diagram the eye can look in any
direction up, down and left to right but the eye’s position horizontally and
vertically must be fixed if one wants to ensure that they are copying the same
image each drawing session. By taping
off one’s toes one ensures that the distance of the eye from the cast remains
constant.¹ Please note that taping off
the horizontal and vertical extremities is usually only applied to cast
drawing. Although one could tape off
where they see the vertical and horizontal extremities on a figure, a figure
moves. But it is useful to tape off
one’s feet when drawing a figure.¹
Measuring (please note that actual perspective was not used in creating this diagram)
The goal of the block-in is to accurately represent the subject they are drawing as it appears on the picture plane.¹ The picture plane can be thought of as an imaginary piece of glass that one views a subject through. The viewer in the illustration above has to look up and down to see the entire box they are measuring. Since the viewer has to look up and down to see the entire box in the illustration above, the overall picture plane that contains the entire image of the large box is as curved as the arc of the viewer's eye that has to look up and down to view the entire box on the wall.¹ This is why one must make sure that the measurements for each section of their cone of vision are parallel to each section of the picture plane in order to make accurate measurements.¹
Measuring at an arm’s length helps to ensure that the distance of the picture plane that one is measuring on remains at a fixed distance from the eye.¹ It is helpful to think of the picture plane that one measures on as a sheet of glass and the block-in just as a representation of the shapes that one sees on that sheet of glass.¹ To this effect when one gets to the point where they are adding up spaces between the lines in their drawing it is helpful to think of it as tapping on the glass of the picture plane instead of just pointing in the air.¹ It is difficult to make sure that one is measuring at a completely parallel angle to their cone of vision but there is a useful trick to making this task easier. According to Andrew McManus, the measuring tool will only appear parallel to one's cone of vision when it reaches its longest length in perspective.²
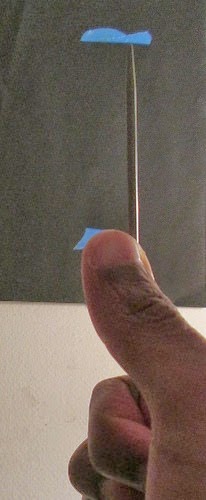

Measuring at an arm’s length helps to ensure that the distance of the picture plane that one is measuring on remains at a fixed distance from the eye.¹ It is helpful to think of the picture plane that one measures on as a sheet of glass and the block-in just as a representation of the shapes that one sees on that sheet of glass.¹ To this effect when one gets to the point where they are adding up spaces between the lines in their drawing it is helpful to think of it as tapping on the glass of the picture plane instead of just pointing in the air.¹ It is difficult to make sure that one is measuring at a completely parallel angle to their cone of vision but there is a useful trick to making this task easier. According to Andrew McManus, the measuring tool will only appear parallel to one's cone of vision when it reaches its longest length in perspective.²


The example above shows how the size of the measuring tool diminishes in perspective as it is turned towards and away from one's eye, even when it is held from the same point. When the measuring tool is longest in perspective, as seen in the middle image above, it is parallel to one's cone of vision.
Keeping the measuring tool parallel to one's eye in perspective also applies to horizontal measurements as well. This is illustrated in the images above.
Keeping the measuring tool parallel to one's eye in perspective also applies to horizontal measurements as well. This is illustrated in the images above.
Here is a demonstration of the practice of comparative
measurement on a Bargue copy.
Block-in Step 1-The Envelope
The first step starts with measuring the actual size of the
longest dimension of the Bargue. It is
easiest to copy shapes when working at actual or sight size. So I made the length of my copy the same length
as the Bargue. Then I used a level to
mark off the top and bottom of my copy with horizontal lines. A level was also
used to make the vertical line. In comparative measurement the longest
dimension on the drawing remains fixed and it is the goal of comparative
measurement to find the measurement of the shorter dimension on the
drawing.
After this, the next step is the envelope. Using a hard sharp pencil (I usually use and H) and thick lines, made from multiple applications of the pencil to the paper, I drew lines that generally envelop the shape of the ear. By using thick sharp lines it is easy for me to use my kneaded eraser to change the sides of the lines I make when I realize that they have to be moved. To keep it simple, it is helpful to use only 3-5 lines for the envelope.¹ The order that I drew these lines in was decided by starting with the lines of the longest dimensions of the ear to get a feel for the overall mass of the shape of the envelope and I then added tilts from there.¹ This same process of laying in shapes from the longest tilts to shorter tilts is followed while laying in all of the shapes throughout the block-in process.¹ It is important to keep the lines straight throughout the entire block-in process to simplify any curves that are seen.¹ The idea is to work from general to specific so using straight lines is very helpful for that. It is also important to let the lines cross over each other throughout the entire block-in process in order to have an easier time of moving their points of intersection while re-arranging shapes.¹
After this, the next step is the envelope. Using a hard sharp pencil (I usually use and H) and thick lines, made from multiple applications of the pencil to the paper, I drew lines that generally envelop the shape of the ear. By using thick sharp lines it is easy for me to use my kneaded eraser to change the sides of the lines I make when I realize that they have to be moved. To keep it simple, it is helpful to use only 3-5 lines for the envelope.¹ The order that I drew these lines in was decided by starting with the lines of the longest dimensions of the ear to get a feel for the overall mass of the shape of the envelope and I then added tilts from there.¹ This same process of laying in shapes from the longest tilts to shorter tilts is followed while laying in all of the shapes throughout the block-in process.¹ It is important to keep the lines straight throughout the entire block-in process to simplify any curves that are seen.¹ The idea is to work from general to specific so using straight lines is very helpful for that. It is also important to let the lines cross over each other throughout the entire block-in process in order to have an easier time of moving their points of intersection while re-arranging shapes.¹
Block-in Step 2-Large Rhythms
Three lines were drawn that indicate large rhythms that run
through entire shape of the cast.
Although measuring will take care of the majority of any placement
issues I tried to be as specific about where I placed these marks because I
have found that the better I start my block-ins the smoother the process of
comparative measurement is.¹ For this
stage one can even face the Bargue and draw a line in the air with their pencil
to get a better feel of a rhythms placement within the envelope.¹ It is very useful in this stage and the previous
stage to simultaneously turn one’s head from the drawing to the Bargue while
still drawing to get a better feel for the angles that the tilts are at.¹
Block-in Step 3- Big Shapes
After I lightened my envelope and large rhythms
by rolling my kneaded eraser into a ball and rolling it on top of the drawing,
I drew the big shapes that I saw in the ear. To keep it simple, it is helpful to only use 3-6 shapes in this stage.¹ Instead of trying to draw abstract shapes or
tilts it is much easier and useful to focus on copying the character of the
shapes that one sees. A great way of
seeing the character in shapes is to think of them as the silhouettes of
cartoon animals. It is much easier to
get an impression of the character of an animal shape than that of an abstract
shape, so I proceed through the entire block-in process with referring to the
shapes that I see as animal shapes and try my best to copy the character of
them. By throwing my eyes out of focus (opening them wide enough to the point where things become slightly blurred) I can better see shapes.¹ It is useful to start with the
most obvious shape that one sees and I tried my best to place it as accurately as
possible within the envelope the I made while using the rhythms as a guide for its
placement.¹
To me this shape was a snake. To get a better idea of the character of different parts of a shape it is useful to think of a different animal shape(s) that characterizes a specific part of a shape.¹ For example, if I was having trouble imagining the snakes tail I could instead think of that area of the shape as a dogs head looking down. I used thick lines to get a general sense of
where the final thin line will be placed.
One is not supposed to think of the final thin line being placed on a
side of this thick line but one is to think of the final thin line eventually
to be placed somewhere in the middle of the thick lines.¹ Please note that while putting in the other
big shapes it is fine if they do not completely adhere to the shape of the
envelope. The envelope is just a try and
since it is usually not 100 percent accurate one must let the animal shapes be
a guide.¹ Also, it is much easier to get
straight lines when focusing on copying the character of the animal shapes
instead of copying tilts. It is very
useful to check the alignment and angles of the animal shapes throughout the
block-in process.¹ To make it easier to compare the shapes in my copy to the shapes on the Bargue I made parts of certain shapes that were not as distinct on the Bargue lighter in my copy.
Block-in Step 4- Halfway Alignment
After the big shapes have been put in I have enough
information in my block in to refer to while checking my measurements. In this stage I aligned the shapes to the halfway
mark of the longest dimension on my drawing to the halfway mark of the longest
dimension on the Bargue. Awareness of
animal shapes is at the core of this measuring process too.¹ Any adjustment to the alignment of shapes to
any measured mark must come with keeping the animal shapes in mind.¹ Since there is room for error with measuring, the animal shapes can be a great guide for letting one know if one's measurement may be off.¹
For example, if it seemed like moving an animal shape much further than
it could possibly move because one's measurement says so it becomes important to
check the measurement multiple times.
When drawing a cast one can’t really place their measuring tool on the cast to find the halfway point but one certainly should place their measuring tool on the drawing to ensure that their measuring and aligning is accurate. To do this properly one has to make sure that they are looking at the extremity of each measurement at eye level. For instance, when I was finding the halfway mark on my drawing I made sure to look at the top and bottom of the measurement on my knitting needle at eye level to make sure that I had a constant measurement.¹ I have found it more useful to mark a line on my knitting needle when trying to find these measurements instead of using my thumb. But there is no remedy for this when measuring the cast. One just has to try their best to keep their extended arm still (even if it means holding one's wrist with their other hand) and make sure that whatever measurement they are referring to goes from the top of their thumbs fingernail to the top of their measuring tool.¹ Because of the inconsistencies in measuring it is necessary to check one’s measurements multiple times while trying to be as precise as possible about them and going with the measurement they find most often.¹ Please note that the colored lines that appear in these photos were not on the Bargue while I was drawing. I used a knitting needle to measure and check alignments. And the horizontal line on my drawing that represents the halfway mark was made with a level to ensure its accuracy.
When drawing a cast one can’t really place their measuring tool on the cast to find the halfway point but one certainly should place their measuring tool on the drawing to ensure that their measuring and aligning is accurate. To do this properly one has to make sure that they are looking at the extremity of each measurement at eye level. For instance, when I was finding the halfway mark on my drawing I made sure to look at the top and bottom of the measurement on my knitting needle at eye level to make sure that I had a constant measurement.¹ I have found it more useful to mark a line on my knitting needle when trying to find these measurements instead of using my thumb. But there is no remedy for this when measuring the cast. One just has to try their best to keep their extended arm still (even if it means holding one's wrist with their other hand) and make sure that whatever measurement they are referring to goes from the top of their thumbs fingernail to the top of their measuring tool.¹ Because of the inconsistencies in measuring it is necessary to check one’s measurements multiple times while trying to be as precise as possible about them and going with the measurement they find most often.¹ Please note that the colored lines that appear in these photos were not on the Bargue while I was drawing. I used a knitting needle to measure and check alignments. And the horizontal line on my drawing that represents the halfway mark was made with a level to ensure its accuracy.
Block-in Step 5- Alignment of Quarters
I now aligned the shapes in my drawing to the quarter marks
on the Bargue. The placement of the initial
big shapes that I put in during step 3 were not too far off so I just used a rolled kneaded eraser to lighten
my initial shapes and re placed them.
But in a situation where the initial shapes are found to be very off
while checking these measurements it is useful to just roll out the initial
shapes with a kneaded eraser, mark off notations of where the shapes now have
to be placed and then re draw them.¹
Note that I am still only using the initial shapes that I
started with. This is because much of
blocking in is about accuracy of the big shapes. Only after I have checked the height to width
and alignment of the drawing do I have the confidence to add more tilts to those shapes.¹
Block-in Step 6- Flipping a dimension
This is the step prior to checking my height to width
measurement. To get a clue as to which
side of my drawing is more off and will most likely have to change to make my
height to width work I flip the longest part of the longest dimension that can be flipped into the
shorter dimension. In this instance, I
flipped the halfway measurement instead of the quarter measurement because the
halfway is long enough to be flipped for it to cross over when checked from the
left and right side on the Bargue. If I
was to flip a quarter, which is not long enough to cross when checked from the
left and right side, I could get the quarters to work well in my drawing and
not be certain of the space in between them.¹
In this instance, I found that the halfway measurement of the height flipped
into the width was much more accurate in my drawing when flipped from the the right side than the left
side. This gave me an idea that the left
side of my drawing may have to move to the right so the halfway flipped from
the left side can touch where it is supposed to.
This guess was confirmed when I checked how the width of
the Bargue flipped into the height of the Bargue. I noticed that the width flipped into the
height on my drawing was much longer than it was supposed to be. I flipped the width into the height from the
top and bottom of the Bargue but in this photo I am just showing the width
flipped from the bottom of the Bargue.
Block-In Step 7- Height to Width
I now moved the left side a bit to the right which made the
halfway flipped from that side touch where it was supposed to and shortened the
width of my drawing so that the width flipped into the height on my drawing
touched where it was supposed to. Overall,
the decision to move a shape should also be based upon seeing it in the animal
shapes and in this instance it did seem like the shape of the left earlobe, that I saw as a snake, could move to the right
so I changed it. One can trust the
relationship of the shorter dimension flipped into the longer dimension if they
have properly aligned the shapes to the halfway and quarter marks in the longer
dimension.¹
Block-in Step 8- Anchor Plumb
The final step of comparative measurement is what Jeremy Deck calls the "anchor
plumb".¹ This stage is to make sure that
even after a proper height to width measurement has been defined that the shapes within are properly aligned.¹ To do this
one must flip a part of the longest dimension into the shorter dimension and
plumb it through the longest dimension.¹ It
is useful to use an anchor plumb that runs through a lot of information on
what one is copying.¹ In this instance, I
flipped a quarter of the longest dimension from the left side of the Bargue. To see how the shapes related to this plumb
on the Bargue I held the point of my knitting needle in between my fingers and
let it dangle which allowed gravity to place it completely vertical.¹ On the drawing I just used a level to make
sure that it plumbed completely vertical.
I then re-organized my shapes around this plumb line. After this one can check the alignment of 1/8th’s
on the longest dimension and can flip the measurements of the 1’4’s and 1’8’s
into the shorter dimension if they want to.
Step 9- Alignment, Angles, Animals
After the anchor plumb is established one can focus completely on the
alignment and angles of the animal shapes without worrying too much about
measuring because the measuring previously used should have properly placed key
points in the drawing.¹ As long as these
key points do not move the block-in can be adjusted without fear of losing
accuracy.¹ Please note, that because there is room for error with measuring the animal shapes are the greatest guide at this point because in the end the
eye is more accurate than any measuring device.¹
To this end, if the shapes seem to need to move beyond the measured
marks a bit it usually is fine as long as they don’t go too far beyond the
measured marks.¹ After the anchor plumb
stage the broad lines can be broken into smaller tilts, while thinking of
adding tilts as adding character to the animal shapes, and using thinner lines to be
more specific.¹ The general rule is to work from general to specific. So the thinness of the line is to correspond to the amount of tilts and shapes that are in the drawing.¹ Also, it is a good idea to make sure that no part of the block-in is advancing too far beyond other parts because it would make it too difficult to compare the different areas that one is working on.¹ (The only exception to this rule is in drawing the figure because it is fine for the drawing of the torso to advance beyond other parts since the torso is the part of a figure that moves the least and the development of other areas should be based around it.) It can be very helpful to
switch to a rubber eraser to thin the line.
The Tombo Mono Zero is a great thin rubber eraser and can be purchased here http://www.jetpens.com/Tombow-Mono-Zero-Eraser-2.3-mm-Circle-Silver-Body/pd/1747 And it can be helpful to lighten a previous attempt by using a rolled
kneaded eraser to roll it out and then try again more specifically with the
pencil on top of it. I find it useful to
plumb just about everything in this stage before thinning my line too much.
Also, after the "anchor plumb" stage it is very useful to think of how the animal shapes relate
to each other by imagining how the different animal shapes are interacting with
each other and checking to see if the same is happening in one’s drawing.¹ Another useful tip is to quickly turn one’s
head from a shape on the Bargue to a shape on the drawing to see if it is
animating or moving more or less than it is supposed to.¹ When drawing a cast with comparative measurement, although the block-in started at an arms length away from the eye by this step the easel is much closer and by the final pass step the front of the easel is to be touching one's feet so one can have a clear view of what they are drawing.¹ When drawing this close the drawing board must be raised or lowered from its original placement so that what one is drawing is at the center of their cone of vision.
Step 10- Final Pass (Conceptual Thinking)
In this stage one focuses more on the three dimensional
reality that the shapes describe. It is
to be thought of as reaching into the picture plane, placing the point of one’s
pencil on the form and running it across the side of the form that the shapes
describe to discover how much the form is advancing and receding in space. One should draw the conceptual pass using the
lines that were made while discovering the placement of the shapes as a
guide.¹ Because it is easy to exaggerate
tilts in this stage it is necessary to check the results of the conceptual pass to animal
shapes to make sure that one is not exaggerating tilts. It is still crucial to use straight lined
even in this stage. It is very difficult to decide on the amplitude of each curve when trying to draw it all
at once so it becomes useful to break up curves into small straight lines as
if the lines were planes in space.¹ The advanced student can apply conceptual
thoughts of anatomy and perspective into the conceptual pass at this stage but
since I am a beginner I only go as far as thinking about planes advancing and receding
in space during the conceptual pass. It
is only when a student has attained a high skill level with measuring and
animal shapes that they can move to anatomical thinking during the conceptual
pass to ensure that their knowledge of anatomy will properly conform to the
visual shapes that one sees. In the end,
knowledge of anatomy is very important, especially for modeling form, and if
one does not immerse themselves in the study of anatomy they can reach a limit by only copying shapes.
Below are some block-ins that I have taken to the conceptual pass stage. Please note, that the light shading of the shadows in these studies was done as a last step. By shading in the shadows the light shapes appear bigger than they actually are. So to give me a greater potential for accuracy in blocking-in I shade the drawing in as a last step and it is only to make the block-in easier to look at. It does nothing to make the block-in more accurate. Also note that for this post and future posts that some of the work that I
have made at school have small areas that my instructors have drawn on
for demonstration purposes.
Tippy casts are a great way to practice
comparative measurement because the shapes become so unfamiliar to a
preconceived understanding of anatomy that one has to focus on the character of
the shapes before them to attain any accuracy. These block-ins were each worked on for a
couple of hours. Jeremy Deck reccomends practicing comparative measurement on cast drawings at life size . So when determining the measurement of the longest dimension when beginning a drawing one can actually place a knitting needle on the cast to ensure that the measurement of the longest dimension is life size.¹ Below are some examples of some tippy casts that I have done.
Blocking in the figure uses the same method of comparative measurement that I have described in the Bargue demonstration. The only difference is that it is very helpful to use the shape of the torso to start because since a figure moves the part of the body that moves the least is the torso. So it is very helpful to get the torso as accurate as possible first and then move out from there.¹ For example, in this figure Bargue copy the first shape that I drew was the shape of the torso.
Below are some of the figure Bargues that I have done.These figure Bargues are just for the practice of seeing how close one can get the animal shapes and measurements within a short time frame so all of these figure Bargues (except for the first one) were done between 4 and 4.5 hours. The timing system that I usually use for these is as follows.
-5min- Envelope and Rythms
-20min- Big Shapes
-20min- Halfway Alignment
-30min- Alignment of Quarters
-30-45min-Height to Width Reorganization
-30min- "Anchor Plumb"
-30min- Alignment of 1/8's
-1hr- Adding tilts
Please note, that because these figure bargues are much too large to be seen in one cone of vision it is useful to place it at a perpendicular angle to one's gaze while copying them. Jeremy Deck (personal communication, 2012) recommeds propping the Bargue on a few pieces of cardboard.
Comparative measurement can also be practiced in a sketchbook through the use of a measuring stick that one can mark measurements on in place of a knitting needle. If this measuring stick has edges that are perpendicular then vertical and horizontal plumbs can be obtained by making sure that the top or side of the measuring stick is parallel with the vertical or horizontal extremities. If the measurement of the longest dimension on the Bargue and on one's copy is the same then the after the block-in is complete its accuracy can be checked on a light box. Or if one does not have a light box the block-in can be checked by overlapping the Bargue and the copy in Photoshop.
Footnotes
¹ Jeremy Deck, personal communication, 2012.
² Andrew McManus, personal communication, 2013.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)